The present study deals with analysis and investigation of the treatment of soap & detergent industry wastewater by ozonation process. The results obtained concerning the optimum conditions of ozone treatment dose and contact time have been used for the removal of parameters such as colour, COD, BOD, TDS and other parameters. The ozonation process for the treatment of soap and detergent wastewater is effective. A dose of 19 mg/L, 21.58 mg/L and 30.70 mg/L ozone gives overall percentage of COD and colour reduction of 50.8%, 53.4%, 60.8% and 52.6%, 57.4%, 61.8% respectively at ozone reaction time. The total COD and color reduction depends on ozone concentration and functional groups present in wastewater. In addition, optimal parameters of ozonation process were determined to be 19 mg/L, 21.58 mg/L and 30.70 mg/L ozone doses. At all three ozone doses the turbidity, COD, BOD, alkalinity, colour and suspended solid removal reached 58.6%, 55%, 55.4%, 32%, 57.2% and 60% under selected conditions, respectively. But in this study, the total solids, total dissolved solids and dissolved oxygen increased up to 8.1%, 54.1% and 36% respectively after ozonation and the odour of wastewater does not change in all investigations. Thus, this study might offer an effective way for wastewater treatment of soap and detergent industry.
Keywords |
| Ozonation, COD, BOD, Colour, Turbidity, Soap and detergent industry, Treatment process |
INTRODUCTION |
| The Present studies include the characterization of
wastewater, containing impurities generated in the
industry from different processing steps and units
of eff1uent treatment plant. Performance appraisal
of each unit of effluent treatment and possibility of
augmentation. Final attention is given on treatability
study of various parameters like COD, BOD TDS, Colour
etc. and compares the effect of Ozone doses with
different reaction contact time. Due consideration is
also given to the comparison of effluent characteristics parameters of effluent treatment plant with
the State Pollution Control Board Effluent Quality
standards discharged in different receiving bodies
as per IS: 2490 (Part-I) 1974 and standards for liquid
effluent for Soap and detergent Industries. Toxicity
tests are also done on treated effluent to study the
effects of treated waste effluent on ecological environment
before disposal. |
| Soap and detergent industry consumes considerable
volume of water for various manufacturing
processes of Soap and detergent production. |
| Water is also used and required for steam generation
and other general purposes. The wastewater
discharged is highly polluted in nature with highly
variable characteristics such as temperature, colour,
total solids, BOD, chemical oxygen demand, anions,
cataions, surfactants. Due to highly polluting nature,
it is not possible to discharge treated and untreated
waste either into water course or on land without
causing great damage. They pose a great problem for
environmental engineers. |
| Ozonation processes have been found to be cost effective,
easy to operate, and energy saving treatment
alternatives. Ozonation processes have been mainly
used for wastewater treatment to decolourisation,
COD removal and separate suspended and/or fatty
particles. The main function of Ozone is to flocculate
colloidal particulates into larger particles that can be
removed by sedimentation or flotation. The mode of
action is generally explained in terms of two distinct
mechanisms: 1) neutralization of negatively charged
colloids by cationic hydrolysis products and 2) incorporation
of impurities in an amorphous hydroxide
precipitate, so-called sweep flocculation. The relative
importance of these mechanisms depends on factors
such as contact time and Ozone dosage. Ozonation
has been used for the treatment of wastewater
discharged from Soap and detergent industry. |
| The objective of the experiments is to investigate
Ozonation followed by disinfection using Ozone
doses with different reaction time for pretreatment of
Soap and detergent industry effluent. The optimum
reaction time values and Ozone dose were determined
for each coagulant. Emphasis will be afforded
to the removal efficiency of the COD, BOD5, TSS,
TDS, alkalinity and Colour. Moreover, characteristics
of the floated and settled sludge were assessed.
Initial investments as well as the operational cost of
the treatment process were estimated. |
Materials and Methods |
Wastewater and analytical methods |
| The source for the collection of wastewater samples
throughout the present studies is the soap and
detergent industry situated in Ujjain city, Madhya
Pradesh (India). The main surfactant used in this
factory, is the anionic surfactant. This factory use
the simple process for manufacturing of white and
black Soap by caustic soda, glycerine and fetty acids,
vegetable, and animal oils all these are makeup in a
big pot. Physico-chemical analyses of 24h composite samples were carried out according to APHA. The
analysis covered chemical oxygen demand (COD),
biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5), total suspended
solids (TSS), suspended solids (SS), total dissolved
solid(TDS), Acidity , Turbidity etc. All the parameter
was determined according to APHA. In this study,
we compare the effect of different Ozone doses like
19 mg/L, 21.58 mg/L and 30.70 mg/L ozone on
wastewater parameter. |
Treatment processes |
| The formation of oxygen into ozone occurs with the
use of energy. This process is carried out by an electric
discharge field as in the CD-type ozone generators
(corona discharge simulation of the lightning), or by
ultraviolet radiation as in UV-type ozone generators
(simulation of the ultraviolet rays from the sun). In
addition to these commercial methods, ozone may
also be made through electrolytic and chemical
reactions. In general, an ozonation system includes
passing dry, clean air through a high voltage electric
discharge, i.e., corona discharge, which creates and
ozone concentration of approximately 1% or 10,000
mg/L. In treating small quantities of waste, the UV
ozonators are the most common, while large-scale
systems use either corona discharge or other bulk
ozone-producing methods. |
Experimental setup |
| The ozonation studies are conducted in a 28 cm long
bubble column reactor of 6 cm diameter by varying
the contact time at different ozone rates at room
temperature. Ozone gas is generated by using Ozone
Generator. The generator produced ozone by the
corona discharge method using the oxygen as feed
gas from an oxygen concentrator. The schematic of
the experimental setup is shown in Figure a. Ozone
generation is determined by measuring the gas flow
rate after calibration. Ozone is supplied at the bottom
of the reactor through a gas diffuser. One ozone trap
containing 2% potassium iodide solution is connected
in series with the reactor in order to collect unreacted
ozone. |
Ozonation Studies |
| The ozonation studies are conducted by varying the
contact time at different ozone rate. All the studies
are conducted in the laboratory at room temperature.
500 mL sample of the soap and detergent wastewater
is filled in the borosil glass bubble column reactor,
which are connected serially with one ozone trap containing 500 mL of 2% solution of aqueous potassium
iodide. Ozone is bubbled through the aeration
port of the reactor with the help of gas diffuser. The
ozone gas is allowed to react with the sample for a
specific time interval and 10 mL sample is withdrawn
at every 2 minutes. The samples are analyzed for
COD, BOD, TDS, TSS, DO and other parameters.
The potassium iodide solution from the ozone trap
is titrated with sodium thiosulphate to determine
the amount of unreacted ozone in the outlet stream.
Knowing the amount of ozone concentration in the
feed gas stream, the amount of consumed ozone in
the reactor is calculated. pH of wastewater is neutralized
by addition of sulfuric acid to the wastewater
and the applied ozone dose is kept constant at 30.70
mg/L. Wastewater parameters are measured at
every 2 minutes. The ozonation reaction is conducted
with different ozone dosing contact time to know
the effect of ozone dose on wastewater parameter
removal. The ozonation reaction is conducted at 19
mg/L, 21.58 mg/L and 30.70 mg/L to know the effect
of ozone dose on wastewater parameters. |
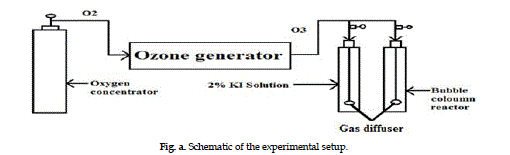
Fig. a. Schematic of the experimental setup. |
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION |
| Studies are carried out in order to investigate the
effect of ozone on the COD, BOD, DO, TDS, TS,
suspended solid, color and Alkalinity reduction of
soap and Detergent industry wastewater and results
obtained are discussed in following sections. Here
all subsequent studies are done without any pH
correction. |
| Influence of reaction time is studied for maximum
reduction of effluent parameters of Soap and
detergent industry wastewater. At neutral pH, ozone
exclusively react with compounds with specific
functional groups through selective direct reactions
such as electrophilic, nucleophilic or dipolar addition
reactions. Under neutral pH, the hydroxide ions catalyze the decomposition of ozone to yield
highly reactive and nonselective hydroxyl radicals,
which have an oxidation potential higher than that
of ozone. The reaction time is varied between 2 to10
min in different experiments to study the influence
of initial reaction time. Figure 1 to 9 shows effluent
parameter’s reduction at different reaction time with
different Ozone doses. The All effluent parameter
reduction at time 10 min was faster than those at
other reaction time. |
Effect of Ozone dose |
| Ozone application rate are varied at 19, 21.58 and
30.70 mg/L to assess the effect of the applied ozone
dosage on COD, BOD and other parameters removal. |
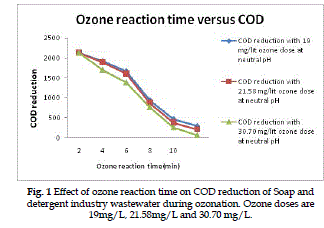
COD Reduction |
| The COD reduction of Soap and detergent industry wastewater as a function of the ozone reaction time
for various ozone doses is present in Fig. 1. The doses
of 19, 21.58 and 30.70 mg/L ozone gives overall
percentage of COD reduction of 50.8%, 53.4% and
60.3% respectively at optimum ozone reaction time.
The Ozone dose kept constant of 30.7mg/L. |
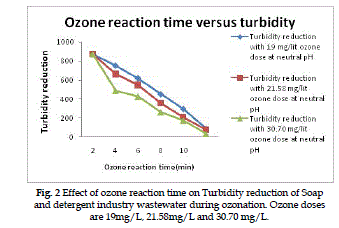
Turbidity reduction |
| The turbidity reduction of Soap and detergent industry
wastewater as a function of ozone reaction
time for various ozone doses is presented in Fig (2).
A dose of 19mg/L, 21.58mg/L and 30.70mg/L ozone
has gives overall percentage of turbidity reduction
is 50.2%, 57.4% and 68.2% respectively at optimum
ozone doses. |
Colour reduction |
| The colour reduction of Soap and detergent industry
wastewater as a function of the initial ozone reaction
time for various ozone doses is present in Fig. (3).
A dose of 19, 21.58 and 30.70 mg/lit gives overall
percentage of colour reduction of 52.6%, 57.4% and
61.8% respectively at optimum ozone doses. |
Total solids increase |
| The total solids increase of Soap and detergent industry
wastewater as a function of the initial ozone
reaction time for various ozone doses is present in Fig.
(4). A dose of 19, 21.58 and 30.70 mg/L gives overall
percentage of increased total solids of 6%, 7.7% and
10.6% respectively at optimum ozone doses. These
percentage values of total solids are increased values
after ozone treatment of untreated wastewater total
solids value. |
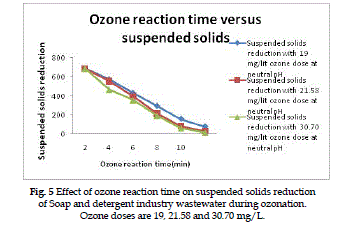
Suspended solids reduction |
| The suspended solids reduction of Soap and detergent
industry wastewater as a function of the initial
ozone reaction time for various ozone doses is present
in Fig. (5). A dose of 19, 21.58 and 30.70 mg/L gives
overall percentage of suspended solids reduction
of 55.2%, 62.8% and 68% respectively at optimum
ozone doses. |
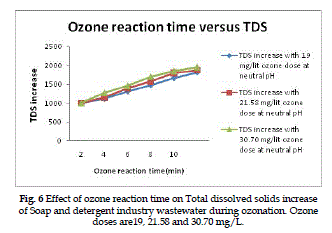
Total dissolved solids increase |
| The total dissolved solids increase of Soap and detergent
industry wastewater as a function of the initial ozone reaction time for various ozone doses is present
in Fig. (6). A dose of 19, 21.58 and 30.70 mg/L gives
overall percentage of increased Total dissolved solids
of 47.88%, 56% and 64.8% respectively at optimum
ozone reaction time. These percentage values of total
dissolved solids are increased values after ozone
treatment of untreated wastewater total solid value. |
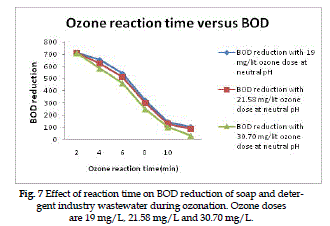
BOD Reduction |
| The BOD reduction of wastewater as a function of
the ozone reaction time for various ozone doses is
present in Fig. (7). The doses of 19, 21.58 and 30.70
mg/L ozone gives overall percentage BOD reduction
of 50.6%, 55.2% and 60.4% respectively at optimum
ozone reaction time. The ozone doses kept constant
of 30.70 mg/L. |
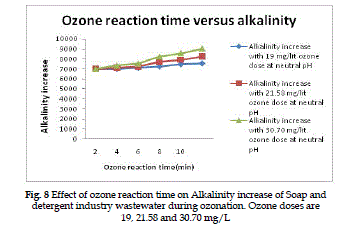
Alkalinity increase |
| The alkalinity increase of Soap and detergent industry
wastewater as a function of the initial ozone
reaction time for various ozone doses is present in
Fig. (8). A dose of 19, 21.58 and 30.70 mg/L ozone
gives overall percentage of alkalinity reduction of
35.6%, 32.4% and 27.8%. |
Dissolved oxygen increase |
| The dissolved oxygen increase of Soap and detergent
industry wastewater as a function of the initial ozone
reaction time for various ozone doses is present in Fig.
(9). A dose of 19, 21.58 and 30.70 mg/L ozone gives
overall percentage of increased dissolved oxygen
of 17.6%, 30.5% and 60% respectively at optimum
ozone doses. These percentage values of dissolved
oxygen are increased values after ozonation process. |
Conclusion |
| 1. The Ozonation process for the treatment of Soap
and detergent industry wastewater is effective.
A dose of 19, 21.58 and 30.70 mg/L gives overall
percentage of COD reduction of 50.8%, 53.4% and
60.8% respectively at optimum ozone reaction time
respectively. COD reduction is found to extremely
depend on ozone doses and reaction time. The total
COD reduction is depending on ozone concentration
and functional groups present in wastewater. |
| 2. The overall percentage of Colour reduction of
52.6%, 57.4% and 61.8% are measured for 19, 21.58
and 30.70 mg/L ozone doses respectively. |
| 3. The overall percent of BOD reduction of 50.6%, 55.2% and 60.4% are measured for 19,
21.58 and 30.70 mg/L ozone doses respectively. |
| 4. The overall percent of Turbidity reduction
of 50.2%, 57.4% and 68.2% are
measured for 19, 21.58 and 30.70 mg/L
ozone doses respectively. |
| 5. The overall percentage of alkalinity
increase of 35.6%, 32.4% and 27.8% are
measured for 19, 21.58, 30.70 mg/L
ozone doses respectively. |
| 6. The overall percentage of total solid
of wastewater are increased from our
actual value up to 6%, 7.7% and 10.6%
are measured for 19, 21.58and 30.70
mg/L ozone doses respectively. |
| 7. The overall percentage of dissolved
oxygen are increased from our actual
value up to 17.6%, 30.5% and 60% are
measured for 19, 21.58 and 30.70 mg/L
ozone doses respectively. |
| 8. The overall percentage of total dissolved
solids are increased from our
actual value up to 47.88%, 54.86% and
64.8% are measured for 19, 21.58 and
30.70 ozone doses respectively. |
| 9. The overall percentage of suspended
solid reduction of 55.2%, 62.8% and 68%
are measured for 19, 21.58 and 30.70
mg/L ozone doses respectively. |
| Based on all the experimental results
it is concluded that the 30.70 mg/L
ozone doses gives the good results as
compared to the 19 mg/L and 21.58
mg/L ozone doses. |
FUTURE SCOPE AND WORK |
| Industrial wastewater treatment generally
has choice between biological and
physico-chemical treatment technology,
whereas, if the industries generate
same characteristics of waste, then the
treatment trains are also almost same
(e.g. Sugar, Dairy, Distillery, Fertilizer
and Textile Industries etc.). However,
this does not hold good for Soap and
detergent industrial waste. This is due
to varying type of Soap and detergent
manufacturing units in different Soap
and detergent industries and therefore,
the waste generated is varying in quantity and quality. |
| 1. The ozonation process has COD
removal capacity hence pre or post
ozonation along with ozonation process
can be used for increasing the removal
efficiency. |
| 2. Ozonation process combined with
Fenton, photo-Fenton, and H2O2/UV
processes are effective for wastewater
treatment of Soap and detergent manufacturer
and Soap and detergent industry. |
| 3. After treatment slight yellow color
remains in the sample, it can be removed
in the ozonation process. |
| 4. BOD removal rate can be increased
by addition of sewage sludge in the
wastewater. |
| 5. The combined ozonation and catalyst
ozonation process for disposal of
Soap and detergent industry wastewater
is much easier to operate and costs much
lower than other processes such as
physical adsorption, chemical oxidation
and conventional biological
process. |
| 6. Ozone as a standalone system or
with UV/H2O2 can remove COD, BOD
from water up to 90%. It also removes
various dyes from the water effectively
up to 99%. Additionally ozone can be
used for cyanide removal from waste
water. Pesticide industry also finds a
wide application of ozone for breaking
down the harmful chemicals in their
wastewater and they are Reduces
Chemical Oxygen Demand, Reduces
Biological Oxygen Demand, Removes
Colour, Reduces Oil and Grease, Removes
Detergents, Reduces Pesticide,
Reduces usage of Harmful Chemicals
and Ecofriendly. |
Tables at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Table 1 |
Table 2 |
Table 3 |
Table 4 |
Table 5 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Table 6 |
Table 7 |
Table 8 |
Table 9 |
|
| |
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
Figure 5 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 6 |
Figure 7 |
Figure 8 |
Figure 9 |
|
| |
References |
- Sheng, H. Lin, Chi, M. Lin and Horng, G.Leu, 1999. Operating characteristicsand kinetic study of surfactant wastewatertreatment by fenton oxidation.Wat. Res. 33 :1735-1741.
- El-Gohari, F.A., Nawar, S.S., Ali, H.I. Treatmentof wastewater from a detergentand soap factory. Water Pollution Control Lab (WPCL), National CenterDokki, Cairo, Egypt.
- Sanz, J., Lombraña, J.I., Ma De Luis, A. andVarona, F. 2003. UV/H2O2 chemicaloxidation for high loaded effluents:A degradation kinetic study of lassurfactant wastewaters. EnvironmentalTechnology. 24 : 903-911.
- Keisuke Ikehata and Mohamed GamalEl-Din, 2004. Degradation of Recalcitrant Surfactants in Wastewater by Ozonation and Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Review, Ozone: Science& Engineering. The Journal of the InternationalOzone Association. 26 : 327-343.
- Jan Perkowski, WojciechJózwiak, Lech Kosand PawelStajszczyk, 2006. Applicationof FentonâÂÂs Reagent in DetergentSeparation in Highly ConcentratedWater Solutions. Fibres and Textiles inEastern Europe. 14 : 114-119.
- Perkowski1, J., Bzdon1, S., Bulska, A. andJózwiak, W.K. 2006. Decompositionof Detergents Present in Car-WashSewage by Titania Photo-AssistedOxidation. Polish J. of Environ. Stud. 15: 457-465.
- Dick Cardis, Cameron Tapp, Marc DeBrumand Rip G. Rice, 2007. Ozone in theLaundry Industry-Practical Experiencesin the United Kingdom, Ozone:Science & Engineering. The Journal ofthe International Ozone Association. 29: 85-99.
- Tekade, P.V., Mohabansi, N.P. and Patil,V.B. 2011. Study of physico chemicalproperties of effluent from soap anddetergent industry in Wardha. RasayanJournal. 4 : 461-465.
- Martins, Rui C., Quinta-Ferreira and Rosa,M. 2011. Comparison of AdvancedOxidation Processes (AOPs) based onO3 and H2O2 for the remediation ofreal wastewaters. Journal of AdvancedOxidation Technologies. 14 : 282-291.
- Martins, R.C., Silva, A.M., Castro-Silva, S.,Garção-Nunes, P. and Quinta-Ferreira,R.M. 2011. Advanced oxidation processesfor treatment of effluents from adetergent industry. Journal of Advanced
|